
- #WINDOWS HOSTS FILE HOW TO#
- #WINDOWS HOSTS FILE DRIVERS#
- #WINDOWS HOSTS FILE MAC#
- #WINDOWS HOSTS FILE WINDOWS#
Add your changes at the bottom of the file.
#WINDOWS HOSTS FILE MAC#
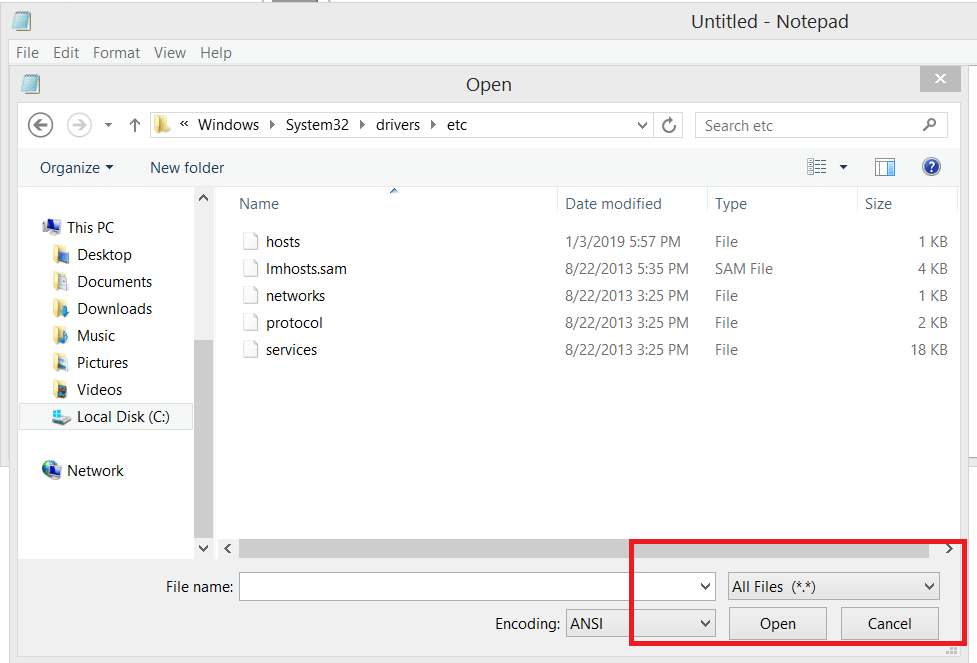
Edit the hosts file with a command line text editor such as nano by typing the following line in the terminal (the command will require your Mac user’s password):.Open Applications > Utilities > Terminal.You should be logged in with a user with administrator privileges on your MAC. Use the Control and X key combination to save the changes.Add the appropriate changes in the hosts file.The command with nano is as follows (the command will require your Linux user’s password): Then click All Files, then Open in the drop-down, and browse the hosts file directory: Now follow the first step and change it to All Files (. Use the nano command line text editor or a different one you have available to open up the hosts file. Start by opening Notepad as administrator.In case Notepad does not show any files in the etc folder, switch the type of file from “Text Documents” to “All Files”. From Notepad, open the hosts file at: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts.Right-click Notepad and select Run as administrator.Use the Search option and search for Notepad.

#WINDOWS HOSTS FILE WINDOWS#
Press the Windows key (previously Start menu).Either: Find the hosts file, right-click, then select Rename. Browse to the file location you used in Step 2. Find the file you just saved, right-click, then select Copy. Enter the file name as hosts, including the quotation marks.
#WINDOWS HOSTS FILE HOW TO#
More detailed instructions on how to locate and edit the hosts file on different operating systems are available below: Windows 8 and 10 In Notepad, go to File menu, then select Save. Once you do that you may need to clear your web browser’s cache, afterward, if you try to reach your domain in a browser it should take you to the site hosted on the server with IP 1.2.3.4. This will “tell” your computer to resolve to 1.2.3.4. In this case, you would need to open up the hosts file with a text editor and append the following line: 1.2.3.4 (Note: Make sure that you don’t have any # signs in front of the IP address as they will deactivate this entry) Let’s say that you wish to resolve to the IP address 1.2.3.4. In the File name field, type C:WindowsSystem32Driversetchosts.
#WINDOWS HOSTS FILE DRIVERS#

TCP\IP under Windows NT allows a computer to communicate over a network with another computer by using either an IP address, a host name, or a NetBIOS name. In Windows XP and higher versions, the hosts file is located in SystemRootsystem32driversetchosts, where SystemRoot is the directory where Windows.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
